Cobalt is used across a variety of industries, but specifically in the production of electric vehicle batteries, airbags, as a drying agent for paints and varnishes, and in dyes and pigments. However, cobalt dust can cause real health problems. The good news is, there are protective measures you can take. Find out more here!

Whether in electric mobility, aviation, or medical technology, cobalt forms an important part of several high-tech products and is used in many industries. But what exactly is cobalt?
Cobalt is a fairly hard, blue-grey metal that occurs naturally in rock, soil, water, plants, and animals. And it is also quite rare. In fact, just 0.0026 % of the earth's crust consists of cobalt.
It is nevertheless common in industry, particularly in the production of batteries for electric vehicles, in aerospace applications, and in the manufacture of cutting tools and catalytic converters. But that’s not all it can be used for. Cobalt is even used as a colouring agent in glasses, ceramics, and porcelain.
Well, sometimes it is, and sometimes it’s not. The thing is, if cobalt is present but not being actively handled or touched, and it doesn't get into the human body, it's not harmful.
But this is somewhat the point.
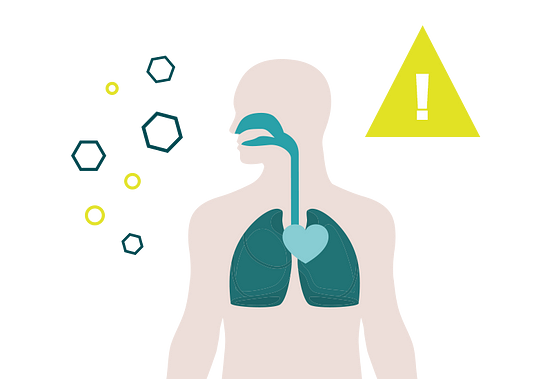
Because when cobalt is used in industry, the processing of the element produces what is known as cobalt dust, which can have serious health consequences for humans.
As the dust is very fine, it can enter the body via the lungs and gastrointestinal tract. Either directly, when breathing in dusty air, or through the intake of water and/or food.
But what happens when the dust is inhaled? The first symptoms are poisoning (nausea, headache, dizziness), which are merely a harbinger of serious secondary illnesses. Immediate breathing problems and long-term, negative effects on the lungs can follow as a result.
When it comes to cobalt, the quantity makes the poison.
In fact, according to a statement released by the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
the amount of inhaled cobalt that remains in the lungs depends on the size of the dust particles. Depending on the solubility, this amount in turn determines the amount that subsequently gets into the blood.
If the particles dissolve faster, the cobalt can pass more easily from the lungs into the blood. If the particles dissolve slowly, they remain in the lungs longer.
Regarding the symptoms, the ATSDR statement added:
“[...] Workers who inhaled air with a cobalt content of 0.038 mg/m³ (about 100,000 times the concentration normally found in the ambient air) for 6 hours then had breathing problems.
“Serious pulmonary effects, including asthma, pneumonia and wheezing, have been reported in those exposed to 0.005 mg cobalt/m3 while working with hard metal, a cobalt-tungsten carbide alloy”.
The UK Health and Safety Executive (HSE) has established clear guidelines to help employers control hazardous substances, such as cobalt.
To reduce the risk of cobalt dust, you as an employer should ensure suitable preventive measures are in place.
These include:
It is also important that employees:
However, the most effective way to mitigate the risk of cobalt dust is by installing an industrial air purification solution.
Protect employees and stay productive at all times
Zehnder Clean Air Solutions extract cobalt dust directly at the source to ensure it is extracted from the air before workers can breathe it in.
This not only helps protect the health of your team and improves productivity, but also ensures a healthy dose of employee retention. The (even) better corporate image will follow along by itself.
To complete your subscription to our newsletter, simply click on the link in your inbox. If you don't receive anything, check your spam folder to be sure.